tests done to look for ovarian torsion|ovarian torsion after hysterectomy : agencies Ovarian torsion is a twisting, or torsion, of the ovary around its ligamentous supports. This may result in loss of blood supply to both the ovary and the fallopian tube. .
WEBDiagnóstico. Tratamento. Pontos-chave. Informações adicionais. Hemorroidas são vasos dilatados do plexo hemorroidário no canal anal. Os sintomas consistem em irritação .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Barbie: Escola de Princesas - assistir online: streaming, compre ou alugue. Você pode assistir "Barbie: Escola de Princesas" no Apple TV, Amazon Video, Google Play Movies para comprar o Download ou no .
The only way to get a definitive diagnosis, though, is for a surgeon to see the twisted ovary inside your body. Often, they use a procedure called laparoscopy to examine your ovaries directly. If they see ovarian torsion during the laparoscopy, they can treat it right away . In one series of 63 patients with suspected torsion, the most sensitive sonographic findings were ovarian edema (sensitivity 85.1 percent and specificity 18.8 percent), abnormal .
An ultrasound (usually a transvaginal one) can confirm the diagnosis. “If a patient has severe pelvic pain and is nauseous and I can feel the cyst during a pelvic exam, we will use transvaginal ultrasound to see if the . CT and MRI are not generally used to diagnose ovarian torsion but are commonly done to rule out other abdominal pathology such as acute appendicitis. The definitive . Ovarian torsion (or adnexal torsion) is a twisting of the ovary (and/or fallopian tube) on its vascular and ligamentous supports, blocking adequate blood flow to the ovary. . Ovarian torsion is a twisting, or torsion, of the ovary around its ligamentous supports. This may result in loss of blood supply to both the ovary and the fallopian tube. .
Ovarian torsion occurs when an ovary becomes twisted around its supporting tissues. Find out why this happens, how to recognize the symptoms, and more.
Diagnosis can be difficult and is mainly based on clinical symptoms and imaging techniques such as ultrasound and MRI. A normal ultrasound scan does not exclude adnexal . Ovarian torsion is a gynaecological emergency: a delay in diagnosis and referral can lead to a reduction in fertility. Ovarian masses are the most common cause of ovarian torsion, but torsion can occur in their absence, .
Ovarian torsion (adnexal torsion) is an infrequent but significant cause of acute lower abdominal pain in women. . Laboratory testing should include a complete blood count (CBC), a complete metabolic panel, and assessment of serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level. . Check that the proper settings are used by looking for flow in the .
Ovarian torsion. Cysts can grow so big that they distort the shape of your ovary, increasing the likelihood that it’ll twist. The twisting can prevent blood flow to your ovary, causing it to die. . Then, they may use the following tests to diagnose an ovarian cyst: Advertisement. A pelvic exam: Your provider will feel inside your pelvis for .
Ovarian torsion - Knowledge @ AMBOSS provides information on the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of ovarian torsion.Ovarian cysts can sometimes also be caused by an underlying condition, such as endometriosis. The vast majority of ovarian cysts are non-cancerous (benign), although a small number are cancerous (malignant). Cancerous cysts are more common if you have been through the menopause. Find out more about the causes of ovarian cysts. Diagnosing .
Ovarian torsion (or adnexal torsion) is a twisting of the ovary and/or fallopian tube on its vascular and ligamentous supports, blocking adequate blood flow to the ovary.Ovarian torsion is a surgical emergency. Rapid diagnosis and intervention are necessary to preserve ovarian function where this is If you have risk factors for ovarian torsion or your OB-GYN suspects it, they will likely perform medical tests. These may include: Blood tests: The OB-GYN may use this approach to check for an infection or signs of a hemorrhage. Pregnancy test: Pregnancy is an ovarian torsion risk factor, so it is useful to confirm it or rule it out. Doppler ultrasound: This .
Tests and procedures used to diagnose ovarian cancer include: Pelvic exam. . Your doctor may recommend testing a sample of your blood to look for gene changes that increase the risk of ovarian cancer. Knowing you have an inherited change in your DNA helps your doctor make decisions about your treatment plan. You may wish to share the .Bottom Line. Ovarian torsions are reported to represent 3% of gynecological emergencies, but the true incidence is largely unknown since many women are likely never diagnosed.For example, the four case series examined at this Journal Club each required many years’ worth of patient data to be reviewed in order to identify a handful of ovarian torsion cases.
Ovarian torsion (or adnexal torsion) is a twisting of the ovary (and/or fallopian tube) on its vascular and ligamentous supports, blocking adequate blood flow to the ovary. Rapid diagnosis and intervention are necessary to preserve ovarian function. Most often seen in women of reproductive age be.What tests should I take? Ultrasound is the first line diagnostic test. There are some ultrasound findings that can help in the diagnosis of adnexal torsion. Unfortunately, blood tests are not useful in the diagnosis of adnexal torsion. Should I undergo surgery? Surgery is recommended if there is suspicion of ovarian torsion. Ovarian torsion rarely presents with classic symptoms. Always consider torsion when evaluating a female patient with abdominal pain, back pain, or flank pain. While US is a great first initial test for the evaluation of both ovarian torsion, do not be reassured by normal dopplers. The most common finding is an ovary > 4cm. CT may as sensitive .
The fallopian tube often twists along with the ovary; when this occurs, it is referred to as adnexal torsion or tubo-ovarian torsion.. The condition can be acute, intermittent or sustained (i.e chronic). Ovarian torsion is a difficult diagnosis to make. US, CT or MRI scanning can assist in diagnosis, but ovarian torsion may ultimately have to be a clinical diagnosis in .
Looking for an easier read? . CT and MRI are not generally used to diagnose ovarian torsion but are commonly done to rule out other abdominal pathology such as acute appendicitis. . The emergency room provider needs to take an accurate history, do a good physical exam, and order the appropriate tests. They also need to coordinate care with . Scrotal complaints are relatively common in the emergency department, comprising at least 0.5% of all emergency department visits. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate the .
A positive pregnancy test does not eliminate the diagnosis of ovarian torsion, especially early in pregnancy, as a corpus luteum cyst may be the source of torsion. Physical exam should include an abdominal exam and a pelvic exam, . Ovarian torsion or rupture can cause severe, intense pelvic or abdominal pain. . Blood and urine tests may be given to check for an alternative diagnosis. Ovarian dermoid cysts don't have diagnostic tumor markers that .
Ovarian torsion (OT) or adnexal torsion is an abnormal condition where an ovary twists on its attachment to other structures, such that blood flow is decreased. [3] [4] Symptoms typically include pelvic pain on one side.[2] [5] While classically the pain is sudden in onset, this is not always the case. [2]Other symptoms may include nausea. [2] Complications may include . An update on the diagnosis and management of ovarian torsion. Georgios Christopoulos MRCOG, Georgios Christopoulos MRCOG. Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK. Search for more papers by this author. Tony Kelly MRCOG, . If you do not receive an email within 10 minutes, your email address may not be registered, and you may need to create a .After evaluating your symptoms and looking at your medical history, your doctor will conduct a pelvic examination to identify any areas of pain or tenderness. They may additionally perform a transvaginal ultrasound to examine your fallopian tube, ovary, and flow of blood. . A doctor may use the following tests to diagnose ovarian torsion .
Tumor marker tests. Blood levels of a protein called a cancer antigen often are elevated in ovarian cancer. If your cyst appears solid and you're at high risk of ovarian cancer, your provider might order a cancer antigen 125 (CA 125) test or other blood tests. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop in or on the ovary . They are common and can happen at any age. Some people with ovarian cysts have pain or pelvic pressure, while others have no symptoms. Fortunately, most ovarian cysts do not require surgical removal and are not caused by cancer. Remember, ovary pain is rarely cancer, but you should see your provider just in case. Your provider may recommend a blood test called a CA-125 test that checks for proteins commonly found in people with ovarian cancer. Ovarian torsion. Ovarian torsion is when your ovary twists around the ligaments that hold it in place.
Ovarian Torsion. Ovarian Torsion is a gynecologic emergency in which the ovary has twisted on its ligaments and blood supply. Rotation of the ovary leads to compression of arteries, veins, and lymphatics causing congestion, ovarian edema, and potentially infarction if untreated. Clinical history is vital in the diagnosis of an adnexal mass (). 4 Risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. The patient's reproductive status and contraception method must be determined .The overall recurrence rate of ovarian torsion is low, ranging from 2% to 12%; although, reportedly, the rate is higher in spontaneously torsed normal adnexa 48 8. Oophoropexy is controversial and current data are insufficient to support performing an oophoropexy to decrease the risk of recurrent ovarian torsion 47 13 44. Here are the signs you might have an ovarian cyst and what you should do if you have one, according to Ob/Gyn Rosanne Kho, MD. Advertisement Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
What is ovarian torsion? Ovarian torsion is a condition that causes twisting of a ligament that supports the ovary. The ovary may also become twisted with the fallopian tube. Blood flow to the ovary is reduced or blocked. The lack of blood flow can cause ovary necrosis (tissue death). Ovarian torsion needs immediate care to prevent this from .
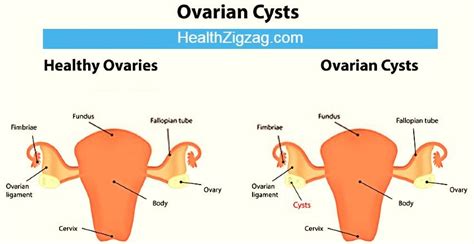
twisted or ruptured ovarian cyst
risk factors for ovarian torsion
Junte-se a nós nessa jornada rumo a um estilo de vida ativo e equilibrado. Seja parte da Allp Fit e descubra o que é ter o melhor ao seu alcance.
tests done to look for ovarian torsion|ovarian torsion after hysterectomy